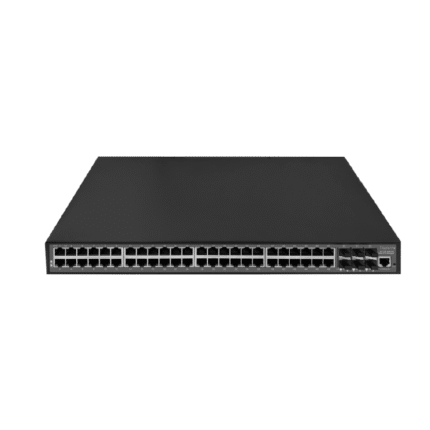
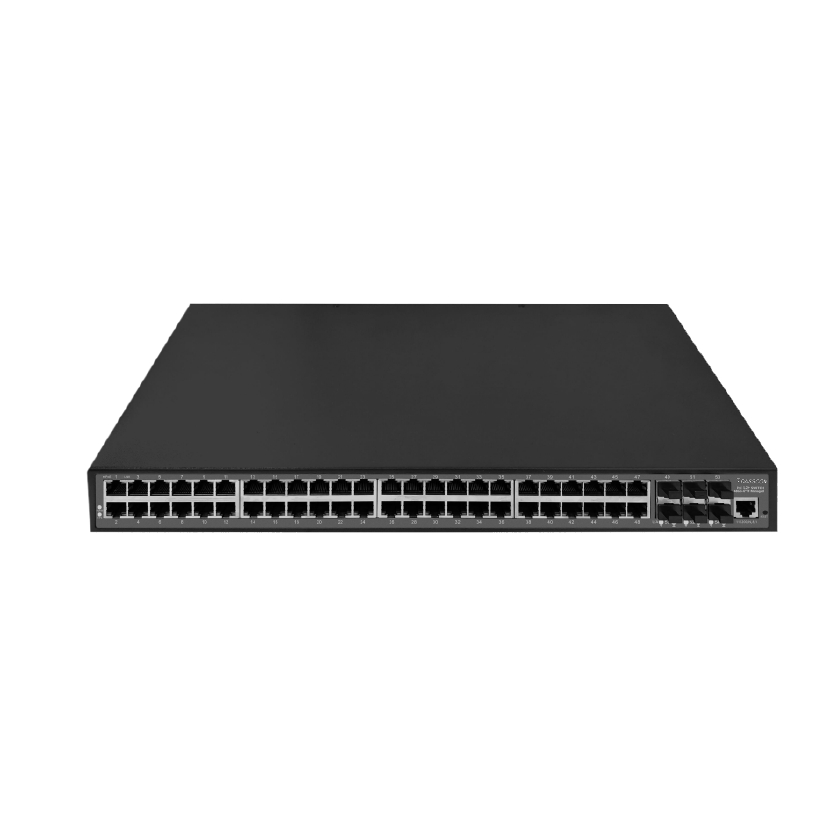
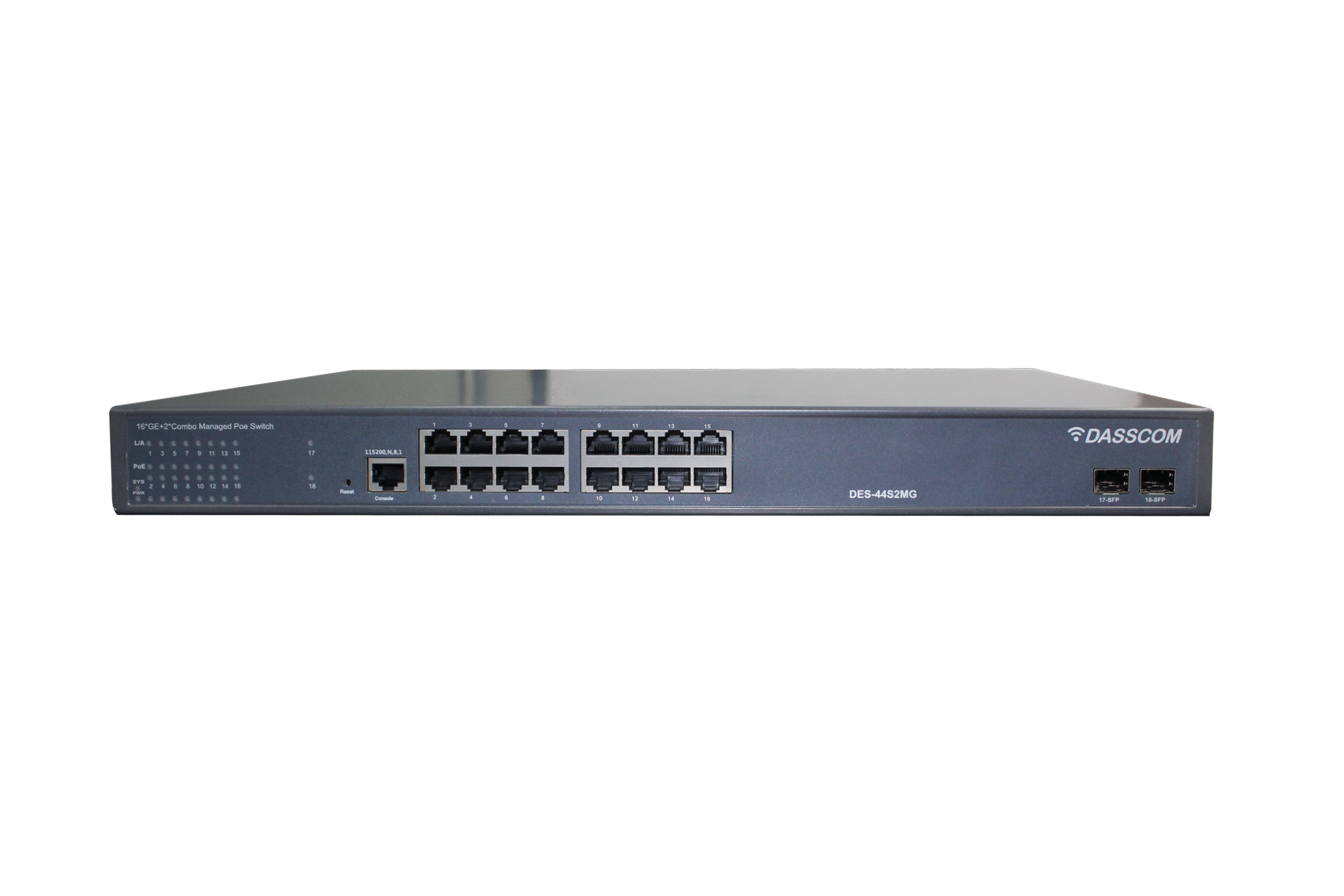
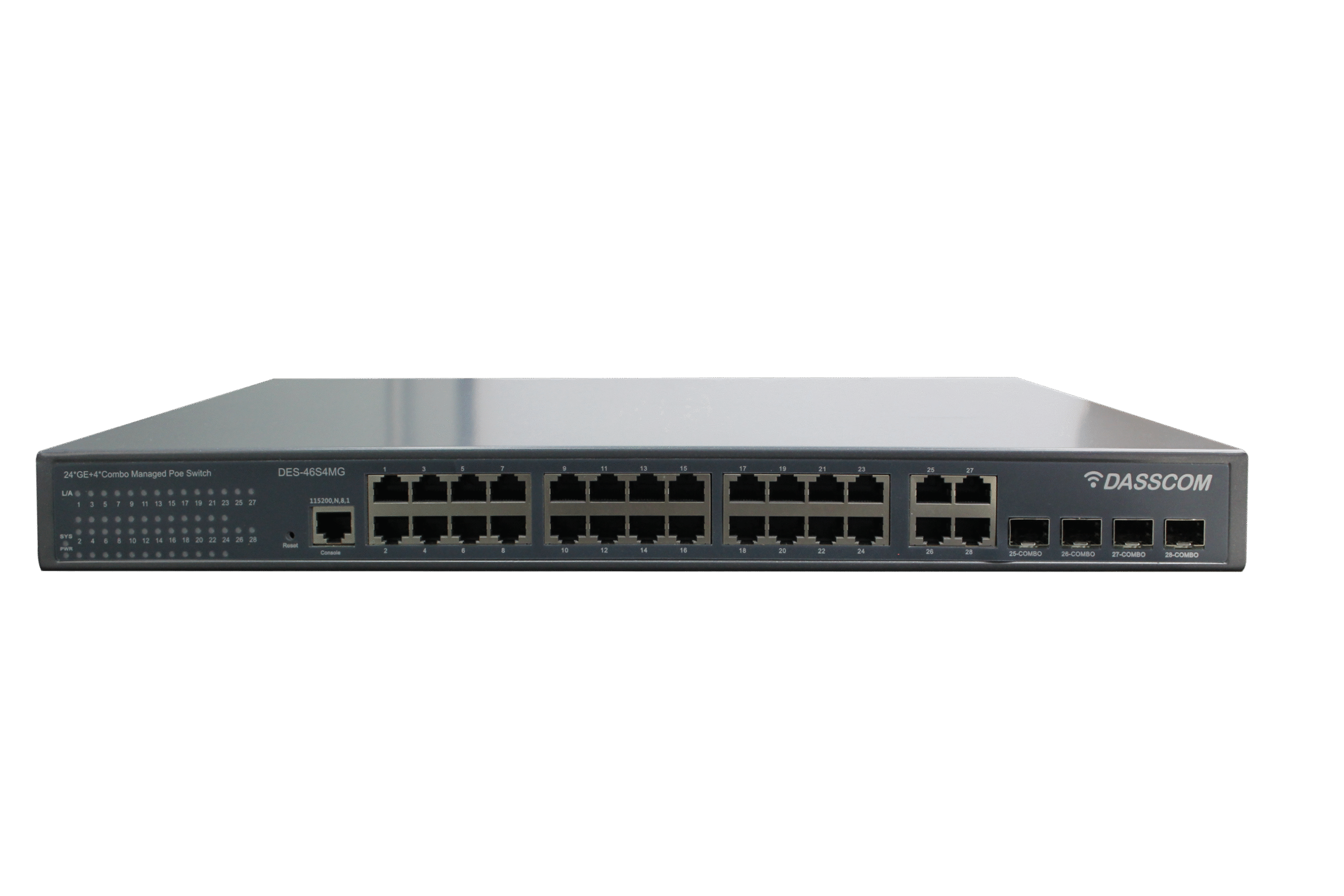
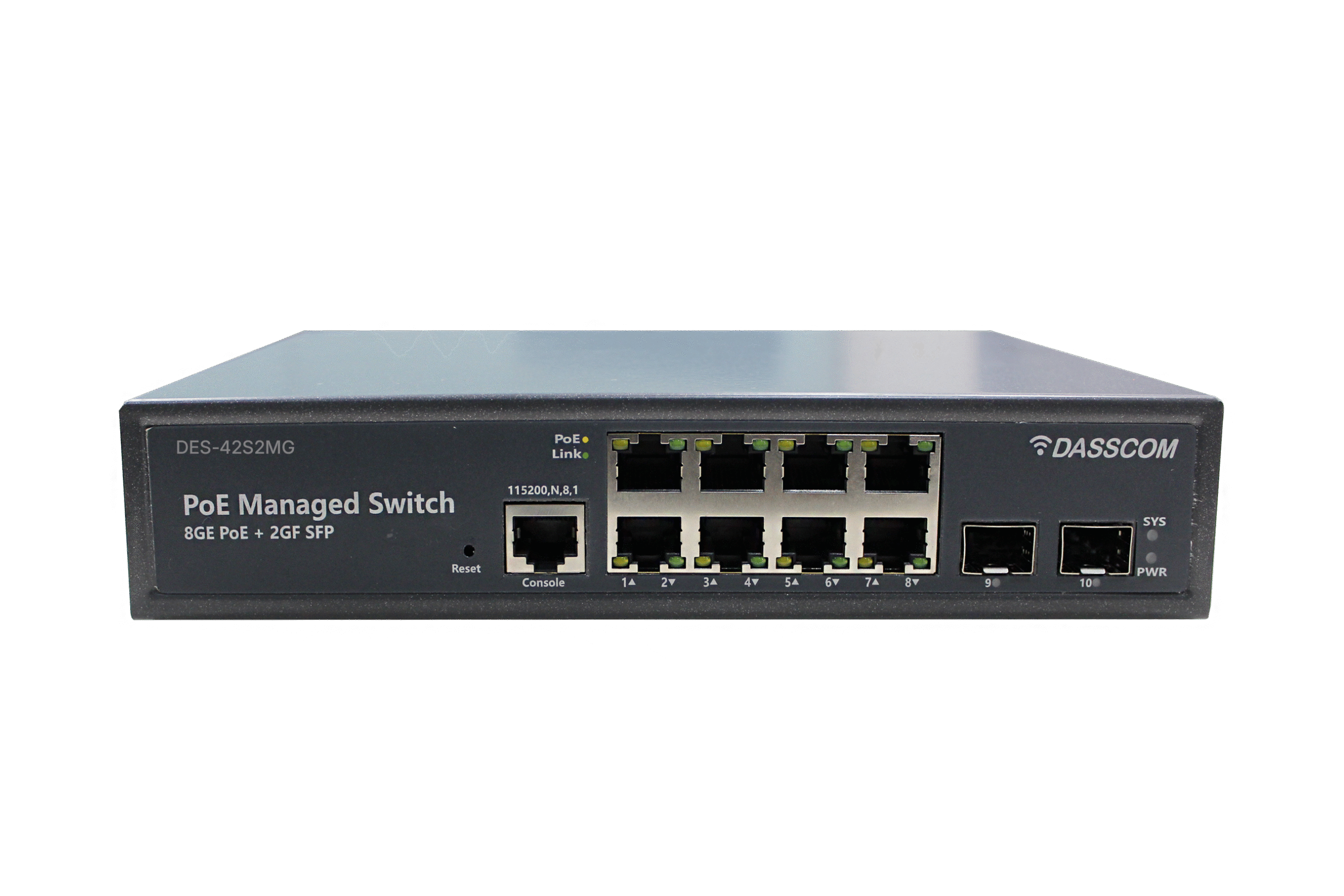
Dasscom’s Managed Switches provide IT teams and network administrators with complete control over network performance, security, and segmentation. Supporting VLANs, QoS, link aggregation, SNMP, and more, these switches are ideal for enterprise networks, VoIP infrastructure, and data-intensive applications. Their intuitive web interfaces and CLI access allow for real-time monitoring and traffic management, while advanced protection features guard against unauthorized access and network loops. Engineered for performance and uptime, Dasscom managed switches ensure stable and scalable connectivity across demanding environments like business campuses, smart buildings, and multi-floor setups.
Exploring the Benefits and Features of Managed Network Switches
In today’s digital-first business environment, data networks are the backbone of every organization. Whether it’s supporting VoIP communication, powering surveillance systems, or enabling smooth IT operations, the quality and efficiency of the network infrastructure determines overall productivity. At the heart of this infrastructure lie managed network switches, devices designed to provide flexibility, security, and control over how data flows through a network.
Unlike unmanaged switches that simply connect devices, managed switches empower IT administrators with advanced configuration and monitoring capabilities, ensuring that the network runs efficiently and securely. Among the most popular choices in enterprise and industrial networks are the 24 port PoE network switch, the manageable ethernet switch, and the smart managed switch. Each of these options is tailored to specific use cases but shares one common goal—optimizing business connectivity.
This blog explores the benefits, technical features, and use cases of managed switches, focusing on why they are essential for modern networking environments.
What are Managed Network Switches?
A managed network switch is a networking device that goes beyond simple data forwarding. Unlike plug-and-play unmanaged switches, it allows administrators to configure VLANs, prioritize traffic (QoS), enable redundancy protocols, monitor performance, and enhance security. This makes manageable switches a vital part of enterprises where uptime, bandwidth allocation, and secure communication are critical.
These switches can be accessed via CLI (Command Line Interface), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), or web-based GUIs. Advanced models, like a managed PoE switch, also provide Power over Ethernet, enabling both data and power to be delivered through the same cable—an essential feature for VoIP phones, IP cameras, and wireless access points.
Key Benefits of Managed Switches
1. Traffic Prioritization (QoS)
A manageable ethernet switch enables Quality of Service, ensuring that time-sensitive traffic like VoIP calls or video conferencing is prioritized over less critical data. This results in better communication quality and fewer disruptions.
2. Scalability
As businesses grow, so does the demand for seamless connectivity. A 24 port PoE network switch can power multiple devices such as surveillance cameras, wireless APs, or VoIP phones—all without requiring additional power adapters. This makes it easier to scale the network as needed.
3. Enhanced Security
Managed PoE network switches provide access control lists (ACLs), port security, and VLAN isolation to prevent unauthorized access. Security policies can be tailored for different users and departments, reducing risks of data breaches.
4. Redundancy and Reliability
Protocols like Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) ensure network redundancy. If one link fails, traffic is rerouted automatically, maintaining uninterrupted connectivity.
5. Remote Management and Monitoring
Through SNMP or web interfaces, administrators can troubleshoot issues, monitor performance, and configure settings remotely. This reduces downtime and helps IT teams maintain efficiency.
Features of Managed PoE Switches
When looking at managed PoE switches, businesses gain the advantage of delivering power and data over a single cable. This simplifies installation and reduces costs in environments where multiple powered devices need connectivity.
Key features include:
- Power Budget Management – The ability to allocate power based on device requirements.
- Device Detection – Automatically recognizes powered devices (PDs) like IP phones, security cameras, or access points.
- Energy Efficiency – Unused ports can be powered down automatically to save energy.
- Centralized Control – With a manageable switch, administrators can monitor both data and power usage in real time.
Why Choose a 24 Port PoE Network Switch?
For medium to large offices, a 24 port PoE network switch strikes the right balance between capacity and scalability. It supports up to 24 devices simultaneously while powering endpoints directly.
Typical use cases include:
- Corporate Offices – Powering VoIP phones and access points.
- Surveillance Systems – Connecting IP cameras without additional power supplies.
- Healthcare – Supporting medical devices and secure communication systems.
- Education – Enabling campus-wide connectivity for smart classrooms.
By deploying a 24 port PoE network switch, businesses ensure flexibility and reduce cabling costs, while still maintaining a robust communication network.
Smart Managed Switches – The Middle Ground
Not every organization requires the full complexity of enterprise-grade managed switches. This is where a smart managed switch comes in. These devices provide key features such as VLAN support, limited QoS, and monitoring capabilities but with simplified interfaces.
A smart managed switch is ideal for:
- Small to medium-sized businesses.
- Branch offices with moderate IT support.
- Networks where basic control and security are required.
While they may not offer the full depth of features as advanced managed PoE network switches, they provide cost-effective solutions for organizations transitioning from unmanaged to managed environments.
Differences Between Managed and Unmanaged Switches
| Feature | Managed Switches | Unmanaged Switches |
| Configuration | Full control via CLI, SNMP, or GUI | Plug-and-play, no configuration |
| Traffic Management | VLANs, QoS, load balancing | None |
| Security | ACLs, port-based security, VLAN isolation | Basic, minimal |
| Cost | Higher, but with greater ROI | Lower upfront cost |
| Use Case | Enterprises, data centers, smart offices | Small networks, home use |
Organizations aiming for reliability and scalability should invest in manageable switches rather than relying on unmanaged options.
Deployment Scenarios
- VoIP Environments – A managed PoE switch ensures that VoIP traffic is prioritized for crystal-clear calls.
- Video Surveillance – A 24 port PoE network switch powers and connects IP cameras with centralized management.
- Smart Campuses – Deploy managed switches for connecting classrooms, labs, and administrative offices securely.
- Industrial Networks – A manageable ethernet switch withstands rugged conditions while ensuring stable connectivity.
Future of Managed Switches
The next generation of manageable switches will incorporate AI-driven network optimization, SDN (Software-Defined Networking), and higher PoE standards (such as PoE++). This evolution will empower businesses with automation, predictive analytics, and greater energy efficiency.
As remote work, IoT, and cloud adoption grow, the role of managed PoE network switches will only become more critical.
Buying Guide – What to Look for in a Managed PoE Switch
When choosing a switch, consider:
- Number of Ports – Options like the 24 port PoE network switch are ideal for scaling businesses.
- PoE Budget – Ensure sufficient power capacity for all connected devices.
- Management Interface – Look for user-friendly GUIs and SNMP support.
- Security Features – VLAN segmentation, port security, and intrusion prevention.
- Redundancy Support – STP, RSTP, and failover protocols.
- Future Scalability – Support for IPv6 and high-speed uplinks (10G or higher).
By investing in the right manageable switch, businesses can secure long-term ROI and smoother operations.
Conclusion
Managed network switches form the backbone of modern IT infrastructure. With features like VLANs, QoS, redundancy, and advanced security, they provide businesses with the control and flexibility needed for uninterrupted communication.
For enterprises requiring scalable connectivity, the 24 port PoE network switch offers power and data in one package. Businesses seeking simplicity with control can benefit from a smart managed switch, while advanced users can maximize network efficiency with a manageable ethernet switch or managed PoE network switch.
In short, managed switches are no longer optional—they are essential for building resilient, secure, and scalable enterprise networks.
FAQs
A managed PoE switch provides both power and data to connected devices while allowing full configuration, monitoring, and security controls—unlike unmanaged switches that operate as simple plug-and-play devices.
A 24 port PoE network switch provides scalability, powering multiple devices such as VoIP phones, wireless access points, and IP cameras, while simplifying installation by eliminating separate power adapters.
A manageable switch allows administrators to control traffic flow, configure VLANs, and monitor network performance, making it essential for enterprises and organizations with high connectivity demands.
A smart managed switch is best for small to medium businesses or branch offices that need essential management features without the complexity of fully managed switches.
By enabling VLAN segmentation, ACLs, and port-based security, managed switches reduce unauthorized access risks and safeguard sensitive business communications.
 Indoor Speakers
Indoor Speakers
 Paging Controller
Paging Controller
 Outdoor Speakers
Outdoor Speakers
 IP Amplifier & Gateway
IP Amplifier & Gateway
 Paging Microphones
Paging Microphones
 Basic IP Phones
Basic IP Phones
 Wifi Phones
Wifi Phones
 Executive IP Phones
Executive IP Phones
 Video Phones
Video Phones

 Duc-series
Duc-series
 FXS/FXO Gateways
FXS/FXO Gateways
 E1/T1 Gateway
E1/T1 Gateway


 Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged Switches
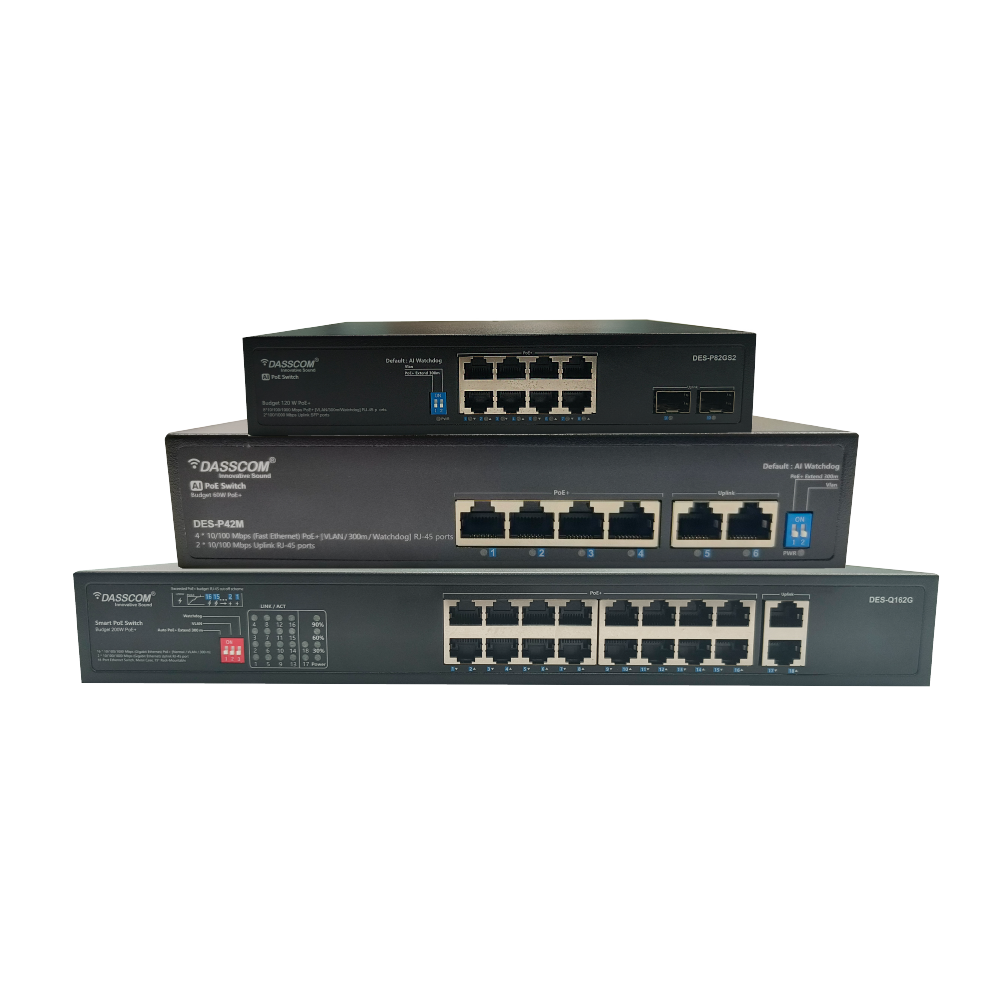
 Managed Switches
Managed Switches
 Industrial Switches
Industrial Switches
 Access Points
Access Points
 Safety Intercoms
Safety Intercoms

 Veda Series
Veda Series
 Divine Series
Divine Series
 Tatva Series
Tatva Series
 VoIP Office
VoIP Office
 Call Center Solutions
Call Center Solutions
 Network Communications
Network Communications
 Public Safety
Public Safety
 Video & Security System
Video & Security System
 Highway Communication
Highway Communication
 Intercom System
Intercom System
 IP Paging Solutions
IP Paging Solutions

 Healthcare
Healthcare
 Hospitality
Hospitality
 School & Universities
School & Universities
 IT Office
IT Office
 SMEs and SMBs
SMEs and SMBs
 Industries
Industries


 Public Address System
Public Address System
 VOIP Phones
VOIP Phones
 VOIP PBX
VOIP PBX
 VOIP Gateways
VOIP Gateways
 Networking Solutions
Networking Solutions
 Call Center Headsets
Call Center Headsets
 Emergency Intercom Stations
Emergency Intercom Stations